After final exam, I decide to do something fun. I know a friend who can remember most of the capitals of countries in the world. So I decided to learn geography. And made a list of places that I wanted to go. With AI, this task took me about 5 hours; however, with the code structure available, we can expand to many other topics such as anatomy, psychology, and many more.
The pipe line is quite simple. We are given a folder of 50_places with sub-folders are the name of each place and a few images. We then create a list of places, parse to geopy to get coordinate. Next, to visualize the location of the place on the map we need to run through cartopy. Now, for content part, we will get the summary from wikipedia. And this task can easily be done by a request from wikiapi.
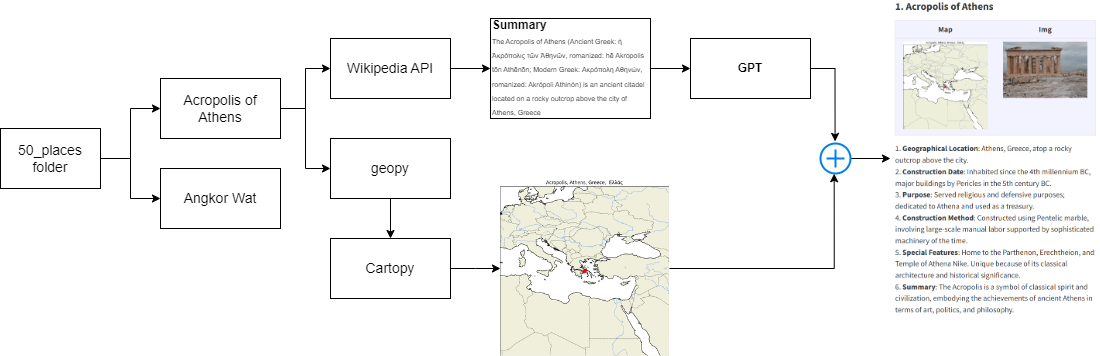
Now, we have real images, map images and content. To make it more concise, I use chatGPT to reformat it. Finally, we can write a script to put images and content together. And the result are shown below.
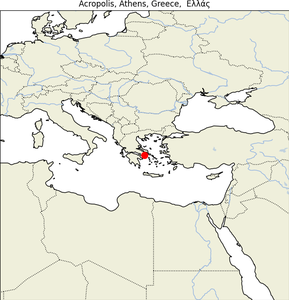
1. Acropolis of Athens
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Athens, Greece, atop a rocky outcrop above the city.
- Construction Date: Inhabited since the 4th millennium BC, major buildings by Pericles in the 5th century BC.
- Purpose: Served religious and defensive purposes; dedicated to Athena and used as a treasury.
- Construction Method: Constructed using Pentelic marble, involving large-scale manual labor supported by sophisticated machinery of the time.
- Special Features: Home to the Parthenon, Erechtheion, and Temple of Athena Nike. Unique because of its classical architecture and historical significance.
- Summary: The Acropolis is a symbol of classical spirit and civilization, embodying the achievements of ancient Athens in terms of art, politics, and philosophy.
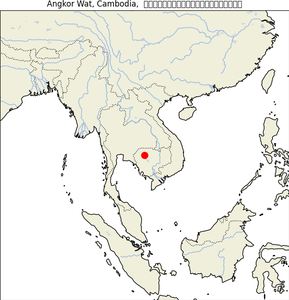
2. Angkor Wat
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Angkor, Cambodia, within the ancient Khmer Empire capital.
- Construction Date: Early 12th century.
- Purpose: Initially a Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu; gradually transformed into a Buddhist temple.
- Construction Method: Sandstone blocks transported from a mountain 50 km away using the river and canals.
- Special Features: The world’s largest religious structure, noted for its vast moat, intricate bas-reliefs, and precisely aligned plan that symbolizes the cosmic world.
- Summary: Angkor Wat combines grandeur with complexity in architecture, extensively decorated with devatas and bas-reliefs, making it a masterpiece of Khmer architecture.
3. Arc de Triomphe
| Map |
Img |
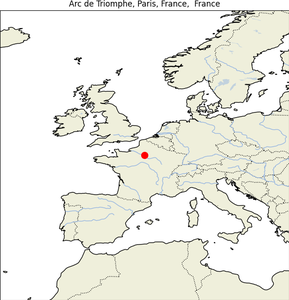 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Center of Place Charles de Gaulle, Paris, France.
- Construction Date: Designed in 1806 and completed in 1836.
- Purpose: Honors those who fought and died for France during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
- Construction Method: Constructed from limestone, with intricate reliefs carved directly into the facades.
- Special Features: Features the names of all French victories and generals inscribed on its surfaces; under its vault lies the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier from WWI.
- Summary: The Arc de Triomphe is an iconic symbol of French nationalism and a prime example of Neoclassical architecture.
4. Atomium
| Map |
Img |
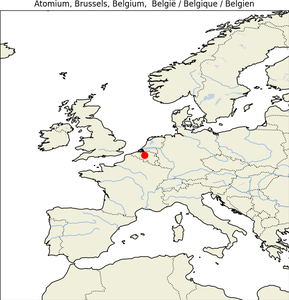 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Brussels, Belgium, specifically at Heysel Park.
- Construction Date: Built in 1958 for the Brussels World’s Fair.
- Purpose: Symbolizes atomic age and scientific progress; now serves as a museum and an exhibition center.
- Construction Method: Composed of nine spheres made of steel, representing an iron crystal magnified 165 billion times.
- Special Features: Stands 102 meters tall, with spheres that contain exhibit halls accessible by escalators running through connecting tubes.
- Summary: The Atomium is a striking example of modernist architecture, reflecting the optimism of the 1950s and Belgium’s industrial and scientific capabilities.
5. Berlin Museum Island
| Map |
Img |
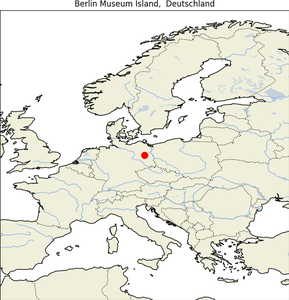 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Part of the Spree Island in the heart of Berlin, Germany.
- Construction Date: Developed from 1830 to 1930.
- Purpose: To house the collections of art and historical artifacts and serve as a public educational institution.
- Construction Method: Built in stages, each museum designed by different architects in Neoclassical, Renaissance, and Baroque styles.
- Special Features: A UNESCO World Heritage site, consists of five museums housing priceless artifacts, including the Bust of Nefertiti.
- Summary: Museum Island is a unique cultural and architectural monument to Germany’s art and history, making it one of the most important museum complexes in the world.
6. Big Ben
| Map |
Img |
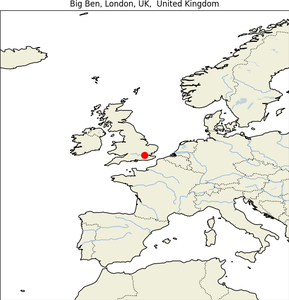 |
 |
- Geographical Location: At the north end of the Palace of Westminster in London, England.
- Construction Date: Completed in 1859.
- Purpose: To house the Great Clock of Westminster and chime the hours; serves as a cultural symbol of the UK and parliamentary democracy.
- Construction Method: Gothic Revival style by architect Augustus Pugin; the clock mechanism was designed to be extremely accurate.
- Special Features: The clock tower is 96 meters tall, with a clock face 7 meters in diameter; it contains the second largest four-faced chiming clock in the world.
- Summary: Big Ben is an emblem of the United Kingdom, renowned for its reliability and the beauty of its design, which has become synonymous with London itself.
6. Blue Mosque
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location on Map
The Blue Mosque, or Sultan Ahmed Mosque, is located in Istanbul, Turkey. The mosque is situated in the Sultanahmet district, which is the historical heart of the city, facing the Hagia Sophia, another magnificent historical site. Here are the approximate coordinates: 41.0054° N, 28.9768° E.
- Construction Date
The construction of the Blue Mosque started in 1609 and was completed in 1617 during the reign of Ottoman Sultan Ahmed I.
- Purpose of Construction
The mosque was built to reassert Ottoman power and serve as a rival to the Hagia Sophia, which faces it directly. It was intended to demonstrate the strength and the artistic achievements of the Ottoman Empire during a period when it was beginning to lose its dominance in various spheres.
- Method of Construction
The Blue Mosque was constructed using traditional Ottoman architecture techniques. It features a large main dome with a diameter of 23.5 meters, flanked by four semi-domes, all supported by four massive piers. The structure is made primarily from cut stone and masonry. The mosque is notable for its six minarets, a number that was originally controversial because it equaled the number at the Mosque of the Kaaba in Mecca. However, a seventh minaret was later added to the Kaaba mosque to resolve the issue.
- Special Features
Iznik Tiles: The mosque’s interior gleams with the blue of the tens of thousands of intricately designed blue Iznik tiles, which cover its galleries and walls.
Minarets: The mosque has six minarets, more than any other mosque in Istanbul at the time of its construction, which was a bold statement of the sultan’s religious and political authority.
Architectural Layout: Its design is the culmination of two centuries of Ottoman mosque development and is a synthesis of the Hagia Sophia and traditional Islamic architecture.
Lighting: The mosque originally had many lamps that were covered in gold and gems. Among the glass bowls one could find ostrich eggs and crystal balls. All these decorations have been removed or pillaged for museums.
- Summary
The Blue Mosque (Sultan Ahmed Mosque) in Istanbul is an iconic symbol of Ottoman architecture and Islamic art. Constructed over the span of eight years, it not only functions as a place of worship but also stands as a major tourist attraction, drawing visitors with its majestic design and beautifully intricate decorations. The mosque’s design features a blend of Byzantine Christian elements and traditional Islamic architecture, making it one of the most photographed sites in Turkey. Its inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage Site list emphasizes its historical and cultural significance.
7. Bodiam Castle
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Near Robertsbridge, East Sussex, England.
- Construction Date: Built in 1385.
- Purpose: Fortified home intended to defend the area against French invasion during the Hundred Years’ War.
- Construction Method: Constructed with a moat and walls with towers at strategic points for defense; built of local stone.
- Special Features: The castle is quadrangular with towers at each corner and a massive gatehouse; it is admired for its picturesque beauty and fairytale appearance.
- Summary: Bodiam Castle is one of the best examples of 14th-century medieval fortress architecture in England, designed both for defense and to impress and intimidate.
8. Brandenburg Gate
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Pariser Platz, Berlin, Germany.
- Construction Date: Constructed between 1788-1791.
- Purpose: Built as a neoclassical triumphal arch to represent peace.
- Construction Method: Built of sandstone; designed by Carl Gotthard Langhans.
- Special Features: Features twelve Doric columns, forming five passageways with the central one reserved for royal processions.
- Summary: The Brandenburg Gate is a potent symbol of German history and unity, having witnessed many of the country’s most significant historical moments, from Napoleon’s passage through it to the fall of the Berlin Wall.
9. Burj Khalifa
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
- Construction Date: Construction started in 2004, completed in 2010.
- Purpose: As a centerpiece of downtown Dubai, it serves as a global icon of architectural innovation and the pinnacle of this new urban world.
- Construction Method: Y-shaped floor plan for residential and hotel usage; the structure is reinforced concrete clad in glass, designed to withstand Dubai’s hot temperature.
- Special Features: At 829.8 meters, it is the tallest building in the world; its design incorporates elements from Islamic architecture.
- Summary: The Burj Khalifa represents a monumental leap in skyscraper engineering and aesthetics, symbolizing the dynamism and scale of Dubai’s economic ambitions.
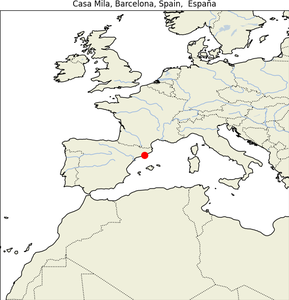
10. Casa Mila
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
- Construction Date: Built between 1906-1912.
- Purpose: Originally a private residence, now a public building showcasing Gaudi’s architectural style and hosting cultural events.
- Construction Method: Notable for its self-supporting stone facade and innovative structural solutions including a unique use of reinforced concrete.
- Special Features: Features an iconic undulating stone facade and twisting wrought iron balconies and windows designed by Josep Maria Jujol.
- Summary: Casa Mila, or La Pedrera, is one of Gaudí’s most ambitious civil buildings and reflects his artistic fullness; it breaks from traditional architecture by using curves to mimic natural forms.
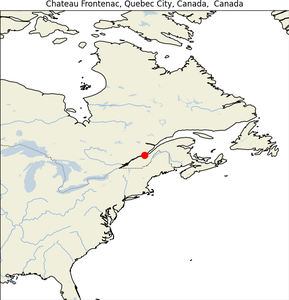
11. Chateau Frontenac
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Quebec City, Quebec, Canada.
- Construction Date: Opened in 1893, expanded in 1993.
- Purpose: Serves as a hotel and a major landmark of Quebec City.
- Construction Method: Châteauesque style designed by Bruce Price; reminiscent of French Renaissance architecture with towering chimneys and steep roofs.
- Special Features: Stands as a grand hotel known for its picturesque setting and is arguably one of the most photographed hotels in the world.
- Summary: The Chateau Frontenac’s architectural style and commanding presence continue to make it a focal point of Quebec City, embodying the area’s rich history and French heritage.
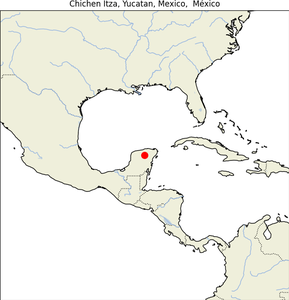
12. Chichen Itza Yucatan Mexico
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location on Map:Chichén Itzá is located in the Tinúm Municipality, Yucatán State, Mexico. It lies in the northern center of the Yucatán Peninsula, about 120 km east of Mérida, the capital of Yucatán. The site is in the northern Maya lowlands region. Here are the approximate coordinates: 20.6843° N, 88.5678° W.
- Construction Date:Chichén Itzá was constructed in phases starting from the Late Classic period (around 600 AD) through the Terminal Classic (around 800 to 900 AD) and into the early Postclassic period (up to around 1200 AD).
- Purpose of Construction:Chichén Itzá was built as a city that served as a major focal point and urban center in the Northern Maya Lowlands. It played a significant role in the political, economic, and ceremonial life of the Maya. It was likely one of the great cities, or Tollans, referenced in Mesoamerican literature and mythology.
- Method of Construction:The city exhibits a variety of architectural styles:
Puuc Style: Characterized by highly decorative masonry and motifs.
Chenes Style: Known for its intricate facades and zoomorphic masks.
Central Mexican Style: This influence suggests cultural diffusion, possibly through trade, rather than direct migration or conquest. The buildings were typically constructed using stone masonry techniques, with large plazas surrounded by tall step pyramids and palaces.
- Special Features:
El Castillo (The Kukulkan Pyramid): A massive step pyramid that dominates the center of Chichén Itzá. It serves as a temple to the god Kukulkan and is famous for the phenomenon of the serpent-shadow during the equinoxes.
The Great Ball Court: The largest and best-preserved ball court in ancient Mesoamerica, used for the Mesoamerican ballgame.
The Temple of the Warriors: An impressive temple complex with a large stepped pyramid, surrounded by rows of carved columns depicting warriors.
Cenotes: Two large natural sinkholes, the Sacred Cenote and the Cenote Xtoloc, which were used for water supply and religious rituals, including human sacrifices.
- Summary: Chichén Itzá, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is one of the most significant and visited archaeological sites in Mexico, attracting millions of tourists annually. This pre-Columbian city showcases a fusion of architectural styles indicative of a rich cultural exchange over centuries. Notably, the site was a major urban center that influenced the economic and ceremonial life in the Maya lowlands. Chichén Itzá’s structures, such as the Kukulkan Pyramid, the Great Ball Court, and the Temple of the Warriors, highlight the technological and artistic advancements of the Maya. Its diverse population contributed to the variety of architectural styles observed, from local Puuc and Chenes styles to Central Mexican influences, reflecting a complex socio-economic network and cultural diffusion rather than direct political control by external forces.
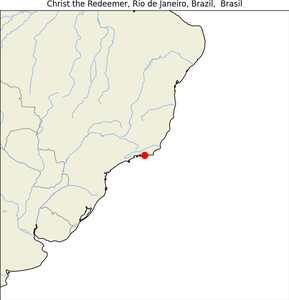
13. Christ the Redeemer
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, atop Corcovado Mountain.
- Construction Date: Constructed between 1922 and 1931.
- Purpose: Serves as a symbol of Christian faith and Brazilian Christianity; reflects the warmth of the Brazilian people who embrace visitors with open arms.
- Construction Method: Made of reinforced concrete and soapstone, designed by Heitor da Silva Costa and sculpted by Paul Landowski.
- Special Features: Stands 30 meters tall, not including its 8-meter pedestal, and its arms span 28 meters wide; one of the New Seven Wonders of the World.
- Summary: Christ the Redeemer is not only a religious symbol but also a cultural icon of Brazil, representing peace and hospitality.
14. Dancing House
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Prague, Czech Republic, on the Rašínovo nábřeží (embankment).
- Construction Date: Completed in 1996.
- Purpose: Originally an office building, now also features a hotel and a restaurant.
- Construction Method: Deconstructivist style by architects Vlado Milunić and Frank Gehry; the building is noted for its unusual shape which resembles two dancers.
- Special Features: The top floor of Dancing House is used as a French restaurant providing magnificent views of the city.
- Summary: The Dancing House is a striking modern architectural feat, known for its innovative and non-traditional design that starkly contrasts with the Baroque, Gothic, and Art Nouveau buildings for which Prague is famous.
15. Dresden Frauenkirche
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Dresden, Germany, at the Neumarkt.
- Construction Date: Originally built in the 18th century and reconstructed from 1994 to 2005.
- Purpose: Serves as a Lutheran church, a symbol of reconciliation, and a major landmark and tourist attraction in Dresden.
- Construction Method: The church was rebuilt exactly as it appeared before its destruction in WWII, using original plans and preserved ruins.
- Special Features: The dome of the Frauenkirche, called the Stone Bell due to its shape, is one of the largest architectural domes in Europe.
- Summary: The Dresden Frauenkirche stands as a testament to Dresden’s resilience and determination to preserve its history and cultural identity despite past devastations.
16. Eiffel Tower
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Champ de Mars, Paris, France.
- Construction Date: Constructed from 1887 to 1889 for the 1889 Exposition Universelle (World’s Fair).
- Purpose: Originally a temporary exhibit for the World’s Fair, it now serves as a global icon of France and a major tourist attraction.
- Construction Method: Designed by Gustave Eiffel, this iron lattice tower was assembled using 18,038 pieces of iron and 2.5 million rivets.
- Special Features: Standing 324 meters tall, it was the tallest man-made structure in the world until the completion of the Chrysler Building in New York in 1930.
- Summary: The Eiffel Tower is renowned not only for its height and distinctive appearance but also for its symbolic representation of modern engineering and beauty.
17. Ephesus
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Near present-day Selçuk, İzmir Province, Turkey.
- Construction Date: Established in the 10th century BC, with significant Roman contributions from the 1st century BC.
- Purpose: Was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city; known for the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
- Construction Method: Constructed with local marble; Ephesus was famous for its Terrace Houses, which featured beautiful mosaics and frescoes.
- Special Features: Includes the Library of Celsus and a large amphitheater that could hold 25,000 people.
- Summary: Ephesus is a key archaeological site, providing insight into the life of early Roman and Greek civilizations through its well-preserved ruins.
18. Flatiron Building
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Manhattan, New York City, at the intersection of Fifth Avenue, Broadway, and East 22nd Street.
- Construction Date: Completed in 1902.
- Purpose: Originally built as an office building, it has become a residential and commercial space that also serves as a cultural icon.
- Construction Method: Designed by Daniel Burnham in the Beaux-Arts style, it utilizes a steel frame with limestone and terracotta facade.
- Special Features: Known for its distinctive triangular shape, resembling a clothes iron.
- Summary: The Flat
19. Gateway Arch
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: St. Louis, Missouri, United States, on the west bank of the Mississippi River.
- Construction Date: Constructed from 1963 to 1965.
- Purpose: Commemorates the westward expansion of the United States; part of the Jefferson National Expansion Memorial.
- Construction Method: Designed by Eero Saarinen, it is a weighted catenary arch made from stainless steel.
- Special Features: At 192 meters, it is the tallest arch in the world and Missouri’s tallest accessible building.
- Summary: The Gateway Arch is a monument to American pioneering spirit, offering expansive views of St. Louis and a museum detailing 19th-century explorations.
20. Giant’s Causeway
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: County Antrim, Northern Ireland.
- Construction Date: Formed 50 to 60 million years ago during volcanic activity.
- Purpose: A natural reserve, it serves as a tourist attraction due to its unique geological features.
- Construction Method: Result of an ancient volcanic eruption that caused molten basalt to crystallize into thousands of hexagonal columns.
- Special Features: Comprises about 40,000 interlocking basalt columns, most of which are hexagonal, and has been declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Summary: The Giant’s Causeway is famed for its striking landscapes and columns, making it one of the most popular natural wonders in the United Kingdom.
21. Golden Gate Bridge
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Spans the Golden Gate, the strait connecting San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean.
- Construction Date: Constructed from 1933 to 1937.
- Purpose: Provides a critical transportation link between San Francisco and Marin County; also serves as a globally recognized symbol of San Francisco and engineering prowess.
- Construction Method: Suspension bridge designed by Joseph Strauss and Irving Morrow; noted for its Art Deco elements and International Orange color.
- Special Features: With a main span of 1,280 meters, it was the longest suspension bridge span in the world at the time of its completion.
- Summary: The Golden Gate Bridge is an iconic American landmark, celebrated for its stunning aesthetics and as a marvel of modern engineering.
22. Guggenheim Museum
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Originally in New York, with subsequent museums in Bilbao, Venice, and Abu Dhabi.
- Construction Date: The original New York museum opened in 1959.
- Purpose: To exhibit the Guggenheim family’s private collection and promote understanding and appreciation of modern art.
- Construction Method: Designed by Frank Lloyd Wright, the New York building is famous for its unique spiral structure which visitors follow as they view the gallery’s artworks.
- Special Features: The New York building is a masterpiece of modern architecture, unique for its spiral ramp and the cylindrical building’s white concrete facade.
- Summary: The Guggenheim Museums are not only centers for the art they house but also architectural landmarks, each designed to reflect a modern aesthetic that complements the art inside.
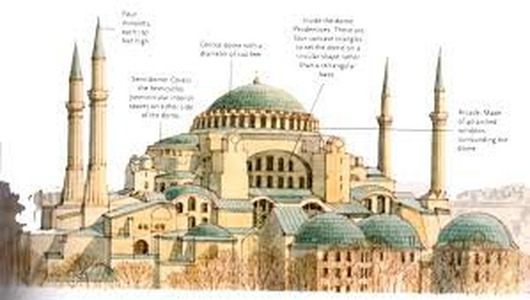
23. Hagia Sophia
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Istanbul, Turkey.
- Construction Date: Completed in 537 AD under the reign of Byzantine Emperor Justinian I.
- Purpose: Originally constructed as an Eastern Orthodox cathedral, it was converted into a mosque after the Ottoman conquest in 1453 and became a museum in the 20th century before being re-converted into a mosque in 2020.
- Construction Method: Famous for its massive dome, it was an engineering marvel of its time, influencing the development of architecture in both the Islamic and Christian worlds.
- Special Features: The interior is adorned with mosaics, marble pillars and coverings, and a vast, expansive nave that exemplifies Byzantine architectural skills.
- Summary: Hagia Sophia is a symbolic monument representing the confluence of the East and West, and Christian and Muslim cultures, making it a significant historical and cultural landmark.
24. Helsinki Cathedral
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Helsinki, Finland.
- Construction Date: Built from 1830 to 1852 as a tribute to Tsar Nicholas I of Russia, who was the Grand Duke of Finland.
- Purpose: Serves as the Finnish Evangelical Lutheran cathedral of the Diocese of Helsinki, a major landmark.
- Construction Method: Constructed in the neoclassical style, its plan is a Greek cross (symmetric in all four directions), topped with a central dome surrounded by four smaller domes.
- Special Features: The cathedral is known for its stark white facade, green dome, and its position overlooking Senate Square, which adds to its visual impact and grandeur.
- Summary: Helsinki Cathedral is not only a place of worship but also a central figure in Helsinki’s urban landscape, symbolizing national and religious significance.
25. Kremlin
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Moscow, Russia, overlooking the Moskva River.
- Construction Date: The current citadel was founded by Ivan III in the late 15th century.
- Purpose: The official residence of the President of the Russian Federation and a historic fortified complex at the heart of Moscow.
- Construction Method: Includes several palaces and cathedrals, enclosed by the Kremlin Wall with Kremlin towers.
- Special Features: The complex serves as the best example of Russian architecture and cultural heritage, containing tombs of Tsars, the State Kremlin Palace, and the Presidential Palace.
- Summary: The Kremlin is not just the political heart of Russia but also a cultural treasure trove, embodying the history and might of the Russian state over centuries.
26. Le_Centre_Pompidou_Paris_France
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
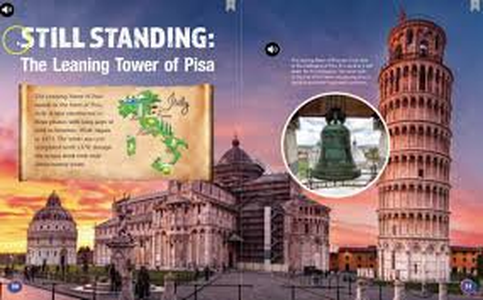
27. Leaning Tower of Pisa
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Pisa, Italy, in the Piazza dei Miracoli.
- Construction Date: Construction began in 1173 and was completed in the 14th century.
- Purpose: Originally intended as the cathedral’s bell tower.
- Construction Method: Built on unstable soil, which caused the tower’s famous tilt. Efforts to correct the inclination only stabilized it, but it continues to lean.
- Special Features: The tower is about 56 meters tall on its highest side and has 294 steps. It is most famous for its unintended tilt.
- Summary: The Leaning Tower of Pisa is a remarkable example of medieval engineering, known globally for its precarious incline and beautiful Romanesque design.
28. Lincoln Center
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Manhattan, New York City, USA.
- Construction Date: Developed during Robert Moses’ urban renewal campaign of the 1950s and 60s.
- Purpose: Home to many of America’s premier performing arts organizations including the Metropolitan Opera, and the New York Philharmonic.
- Construction Method: A masterpiece of Modernist architecture, it features a unified campus of buildings arranged around two main plazas.
- Special Features: Known for its Waterford crystal chandelier, iconic Revson Fountain, and the sprawling Josie Robertson Plaza.
- Summary: Lincoln Center is a focal point for performing arts in America, offering a wide array of performances in its architecturally distinct venues.
29. Machu Picchu
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Cusco Region, Peru, above the Sacred Valley.
- Construction Date: Built in the 15th century, during the reign of Inca emperor Pachacuti.
- Purpose: Likely used as a royal estate and religious retreat for the Inca leadership.
- Construction Method: Built using dry-stone wall technique; stones were fit together without mortar, exemplifying the Incas’ sophisticated engineering skills.
- Special Features: Its location is particularly strategic, being surrounded by agricultural terraces and watered by natural springs.
- Summary: Machu Picchu is one of the most intact Inca ruins, providing insight into the Inca civilization and offering stunning views of the surrounding mountainous landscape.
31. Milan Cathedral
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Milan, Italy.
- Construction Date: Construction began in 1386 and continued sporadically until 1965.
- Purpose: The cathedral church for the Archdiocese of Milan, dedicated to St. Mary of the Nativity.
- Construction Method: Notable for its flamboyant Gothic style, characterized by a forest of spires and an enormous number of statues.
- Special Features: The cathedral’s stunning facade and the Madonnina’s spire, topped with a statue of the Virgin Mary that shines brightly above the city.
- Summary: Milan Cathedral is a monumental structure that dominates the Milanese skyline, embodying the grandeur of Gothic architecture and the spiritual heart of Milan.
32. Millau Bridge
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Near Millau in southern France, crossing the River Tarn.
- Construction Date: Opened in 2004.
- Purpose: To alleviate traffic congestion and shorten travel time between Paris and Béziers and Montpellier.
- Construction Method: A cable-stayed bridge designed by engineer Michel Virlogeux and architect Norman Foster, known for its masts reaching higher than the Eiffel Tower.
- Special Features: The highest bridge tower in the world at 343 meters above the base of the structure.
- Summary: The Millau Viaduct is a feat of modern engineering, noted not only for its record-breaking height but also for its aesthetic grace and minimal environmental impact.
33. Mont Saint-Michel
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Normandy, France.
- Construction Date: The abbey was founded in the 10th century; the current Gothic structure primarily dates from the 13th century.
- Purpose: Initially founded as an abbey, it has served various functions including a pilgrimage site, a prison, and now a historic monument and tourist attraction.
- Construction Method: Built on a rocky island using Gothic architectural techniques, designed to withstand the area’s extreme tides.
- Special Features: Known for its dramatic location and the extreme tides that can vary greatly, at roughly 14 meters between high and low water marks.
- Summary: Mont-Saint-Michel is an iconic symbol of French national identity and a testament to medieval engineering and architectural prowess.
34. Musée d’Orsay
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Paris, France, along the banks of the Seine River.
- Construction Date: The original station was built in 1900 and converted to a museum which opened in 1986.
- Purpose: Houses French art dating from 1848 to 1914, including paintings, sculptures, and photography, showcasing works from the realism period to impressionism and beyond.
- Construction Method: The museum is housed in the former Gare d’Orsay, a Beaux-Arts railway station designed by Victor Laloux.
- Special Features: Known for its vast collection of impressionist and post-impressionist masterpieces by painters such as Monet, Manet, Degas, and Van Gogh.
- Summary: The Musée d’Orsay is renowned not just for its stunning collection of French art but also for its unique architectural adaptation of a former railway station into a world-class museum.
35. Musée du Louvre
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Paris, France, on the Right Bank of the Seine.
- Construction Date: Originally a fortress built in the late 12th century under Philip II; the present structure has evolved since then with significant additions and alterations over the centuries.
- Purpose: Serves as a central landmark of Paris and houses 35,000 works from prehistory to the 21st century.
- Construction Method: The palace has expanded from its medieval fortress origins to the sprawling renaissance and classical style palace it is today.
- Special Features: The Louvre Pyramid, designed by I.M. Pei, is one of the most recognized modern entrances to a museum, contrasting with the classic French Renaissance architecture.
- Summary: The Louvre is not only the world’s largest art museum but also a historic monument in Paris, famed for its art collections that span thousands of years and from across the globe.
36. Neuschwanstein Castle
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Bavaria, Germany, near Füssen.
- Construction Date: Construction started in 1869 but the castle was never fully completed.
- Purpose: Commissioned by Ludwig II of Bavaria as a retreat and as a tribute to Richard Wagner, the composer.
- Construction Method: The castle design incorporates Romanesque Revival style, featuring opulent interior designs and intricate murals depicting Wagnerian themes.
- Special Features: Neuschwanstein is one of the most photographed buildings in the world due to its fairy-tale appearance and also inspired Disneyland’s Sleeping Beauty Castle.
- Summary: Neuschwanstein Castle embodies the romance and mystique of 19th-century Bavaria, combining the king’s love of art and operatic themes with breathtaking alpine landscapes.
37. Osaka Castle
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Osaka, Japan.
- Construction Date: Originally built in 1583 by Toyotomi Hideyoshi.
- Purpose: Played a major role in the unification of Japan during the Azuchi-Momoyama period.
- Construction Method: Features a network of stone fortifications and the central tower built on a plot of elevated land surrounded by defensive walls and moats.
- Special Features: The castle’s main tower is adorned with gold leaf decorations and houses a museum with artifacts from the castle’s history and the Toyotomi period.
- Summary: Osaka Castle is a historic landmark known for its architectural beauty and its significance in the history of Japan, symbolizing the unification and historical power struggles of feudal Japan.
38. Oxford University
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Oxford, England.
- Construction Date: Teaching existed at Oxford in some form in 1096 and developed rapidly from 1167 when Henry II banned English students from attending the University of Paris.
- Purpose: One of the world’s leading universities, known for excellence in scholarship and notable alumni, including numerous UK Prime Ministers and international leaders.
- Construction Method: Comprises 39 autonomous colleges spread across the city center, with buildings showcasing a range of architectural styles from medieval to modern.
- Special Features: The university is known for its unique college system and its historical contributions to education and society.
- Summary: Oxford University is not just a place of learning but a historic institution that has contributed to society through education, research, and cultural influence over many centuries.
39. Sagrada Familia
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
- Construction Date: Construction began in 1882 and is ongoing, with completion targeted for 2026.
- Purpose: This basilica is Antoni Gaudí’s masterpiece, and it combines elements of Gothic and Art Nouveau forms.
- Construction Method: Utilizes modernist architectural techniques, with an emphasis on rich symbolism and complex geometries typical of Gaudí’s style.
- Special Features: Famous for its towering spires, intricate facades, and extensive use of colored glass and sculptured stone.
- Summary: The Sagrada Familia is a testament to Gaudí’s innovative architectural style and remains one of the most detailed and ambitious building projects, reflecting deep religious themes and the artist’s unique approach.
40. Space Needle
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Seattle, Washington, USA.
- Construction Date: Built for the 1962 World’s Fair.
- Purpose: Serves as an observation tower and an iconic symbol of Seattle.
- Construction Method: The tower’s futuristic design features a flying saucer-like observation deck and a slender supporting column.
- Special Features: Stands 184 meters high, with a revolving restaurant at the top providing panoramic views of the surrounding area.
- Summary: The Space Needle is recognized globally as the symbol of Seattle, embodying innovation and the spirit of the Pacific Northwest.
41. Statue of Liberty
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Liberty Island, New York Harbor, USA.
- Construction Date: Dedicated on October 28, 1886.
- Purpose: A gift from the people of France to the USA; symbolizes freedom and democracy.
- Construction Method: Designed by Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi and built by Gustave Eiffel, the statue is made of a copper skin over a framework of steel.
- Special Features: Features a robed female figure representing Libertas, the Roman goddess, holding a torch above her head with her right hand.
- Summary: The Statue of Liberty is not only an icon of freedom and the United States but also a welcoming sight to immigrants arriving from abroad, representing hope and opportunity.
42. Sultan Ahmed Mosque
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Istanbul, Turkey.
- Construction Date: Built between 1609 and 1617 during the rule of Ahmed I.
- Purpose: Known as the Blue Mosque, this historic mosque is a functioning place of worship and a major tourist attraction.
- Construction Method: Classic Ottoman mosque architecture featuring a central dome flanked by secondary domes, semi-domes, and minarets.
- Special Features: Famous for its blue tiles surrounding its interior walls and the use of light to create an interior that glows with a luminous blue hue.
- Summary: The Sultan Ahmed Mosque stands as a superb example of Islamic architecture in Turkey and is particularly noted for its majestic minarets and grand scale.
43. Sydney Harbour Bridge
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, spanning Sydney Harbour.
- Construction Date: Constructed from 1923 to 1932.
- Purpose: Connects the Sydney central business district (CBD) and the North Shore; facilitates vehicular, rail, bicycle, and pedestrian traffic.
- Construction Method: A steel through arch bridge, known for its massive double piers at each end and its iconic arch design.
- Special Features: Often nicknamed “The Coathanger” because of its arch-based design; it’s the sixth longest spanning-arch bridge in the world.
- Summary: The Sydney Harbour Bridge is not only a major transport artery but also a symbol of Sydney and Australia, significant for its engineering merit and stunning aesthetics.
44. Sydney Opera House
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, on Bennelong Point in Sydney Harbour.
- Construction Date: Designed by Jørn Utzon and opened in 1973.
- Purpose: Performs multiple venue performances, including opera, theatre, music, and dance.
- Construction Method: Famous for its unique use of a series of gleaming white sail-like shells as its roof structure, which was a groundbreaking piece of architectural design at the time of construction.
- Special Features: Includes multiple performance venues and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site as of 2007 due to its architectural innovation and beauty.
- Summary: The Sydney Opera House is one of the 20th century’s most famous and distinctive buildings, a masterpiece of modern architectural design, reflecting creativity and innovation.
45. The Great Sphinx
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Giza, Egypt.
- Construction Date: Believed to have been built by Pharaoh Khafre around 2558–2532 BC.
- Purpose: Serves as a guardian statue for the Giza Pyramid complex.
- Construction Method: Carved directly from the bedrock of the Giza plateau, the Sphinx is a monolith sculpture featuring a lion’s body and a human head (believed to be that of Pharaoh Khafre).
- Special Features: One of the world’s largest and oldest statues, it is renowned for its grand scale, mystery surrounding its construction and purpose, and its weathered visage.
- Summary: The Great Sphinx of Giza is an enduring symbol of Egypt’s ancient glory, representing the strength and wisdom of the pharaohs.
46.The Pyramids of Giza
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
47. Tian Tan Buddha
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: Ngong Ping, Lantau Island, Hong Kong.
- Construction Date: Completed in 1993.
- Purpose: Also known as the Big Buddha, it symbolizes the harmonious relationship between man and nature, people and faith.
- Construction Method: A large bronze statue of Buddha Shakyamuni, seated and facing north to look over the Chinese people.
- Special Features: The statue is 34 meters high and weighs over 250 metric tons, making it one of the largest seated Buddha statues in the world.
- Summary: The Tian Tan Buddha is not only a major center of Buddhism in Hong Kong but also a popular tourist attraction, known for its serene location and impressive craftsmanship.
48. Tower Bridge
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: London, England, spanning the River Thames near the Tower of London.
- Construction Date: Constructed from 1886 to 1894.
- Purpose: Facilitates road and pedestrian circulation and features a bascule bridge which is raised to allow ships to pass.
- Construction Method: Victorian Gothic style to harmonize with the nearby Tower of London, the bridge is a combined bascule and suspension bridge.
- Special Features: The bridge’s towers are tied together at the upper level by two horizontal walkways, designed to withstand the horizontal forces exerted by the suspended sections of the bridge.
- Summary: Tower Bridge is one of London’s most famous landmarks, notable both for its unique design and its role as a functional piece of the city’s infrastructure.
49. Washington Monument
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: National Mall in Washington, D.C., USA.
- Construction Date: Construction began in 1848 and was completed in 1884.
- Purpose: Built to honor George Washington, the United States’ first president.
- Construction Method: Constructed of marble, granite, and bluestone gneiss; it’s the world’s tallest predominantly stone structure and the world’s tallest obelisk at 169 meters.
- Special Features: It’s an obelisk-shaped monument, and it once held the title of the tallest structure in the world.
- Summary: The Washington Monument is an iconic symbol of the United States’ national pride and the enduring legacy of President George Washington.
50. White House
| Map |
Img |
 |
 |
- Geographical Location: 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW, Washington, D.C., USA.
- Construction Date: Built between 1792 and 1800; has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams.
- Purpose: Official residence and administrative headquarters of the President of the United States.
- Construction Method: Neoclassical style, designed by James Hoban, made from white-painted Aquia Creek sandstone in the late Georgian style.
- Special Features: The White House includes the Executive Residence, West Wing, East Wing, the Eisenhower Executive Office Building, and the Blair House, a guest residence.
- Summary: The White House is not only an iconic building of political power and the home of the U.S. president but also a symbol of the American government.





































































































